Heart electrical system
The heart has two major jobs:
- It pumps blood to the lungs so they can add oxygen to the red blood cells and
- It pumps the oxygenated blood to the rest of the body.
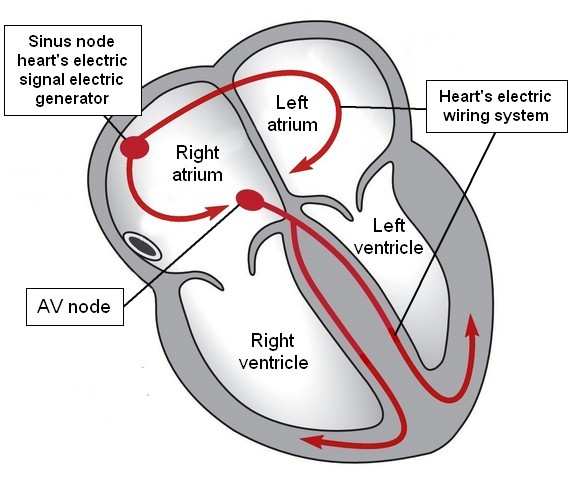
The heart has 4 chambers to pump blood: two atriums and two ventricles. The heart muscle squeezes these chambers when electricity enters the muscle which then pumps the blood. For the heart to work well: the chambers of the heart must pump at the right time. To coordinate the pumping the heart uses an electrical system. In a normal healthy heart the electricity starts in what is called the ‘Sinus Node.’ This node acts as a natural “pacemaker” for the heart and causes it to beat from 60 to 100 times per minute.
The electricity that starts in the Sinus Node travels through to the muscles of the heart via the heart’s complex electrical system. The diagram below outlines the major parts of the electrical system.
What is an Electrocardiogram (ECG)
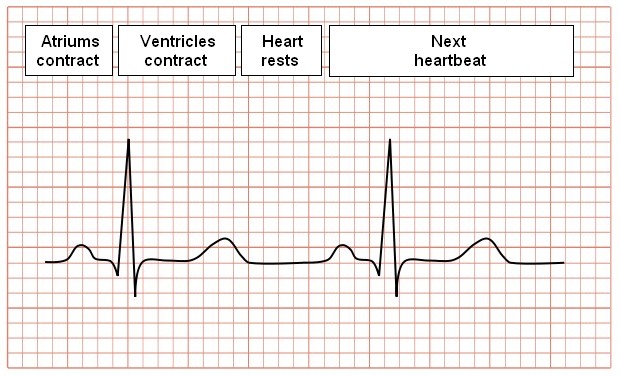
An electrocardiogram (ECG) records the electrical activity of the heart. The electric impulses produced by the heart can be detected by the ECG machine. ECG is one of the oldest tests and most important tests in cardiology helping doctors to find the cause of symptoms such as palpitations or chest pain. Every heartbeat is described on an ECG as an electrical signal representing each part of the heart.
Next article: